ETF vs Mutual Fund: Guide for Investors in 2026
Investing can sometimes feel confusing, especially with options like ETFs and mutual funds. You may have heard about ETFs Vanguard, ETFs BlackRock, or ETFs gold, but not been sure which is better. This guide will break down ETF vs mutual fund in simple, friendly terms so you can make informed investment decisions in 2026.
What is an ETF and How It Works
An ETF, or Exchange-Traded Fund, trades on the stock market just like a regular stock. When you buy an ETF, you are investing in a basket of assets, such as stocks, bonds, or commodities like gold. ETFs combine diversification with flexibility.
Examples include:
- ETFs stock – invest in hundreds of companies in one purchase
- ETFs gold – gain exposure to gold prices without owning physical gold
- ETFs Vanguard – low-cost, diversified ETFs like Vanguard S&P 500 ETF
- ETFs BlackRock – iShares ETFs providing global market exposure
ETFs are traded throughout the day, unlike mutual funds which are priced at the end of the trading day, giving you flexibility to buy or sell at almost any time. They are also generally tax-efficient with lower fees.
What is a Mutual Fund
A mutual fund pools investor money and is managed by a professional fund manager. The manager decides which assets to buy and sell according to the fund’s strategy. Mutual funds are priced at the end of each trading day.
Mutual funds can be actively managed or passively managed like index funds. They are ideal for investors who prefer professional management but may come with higher fees.
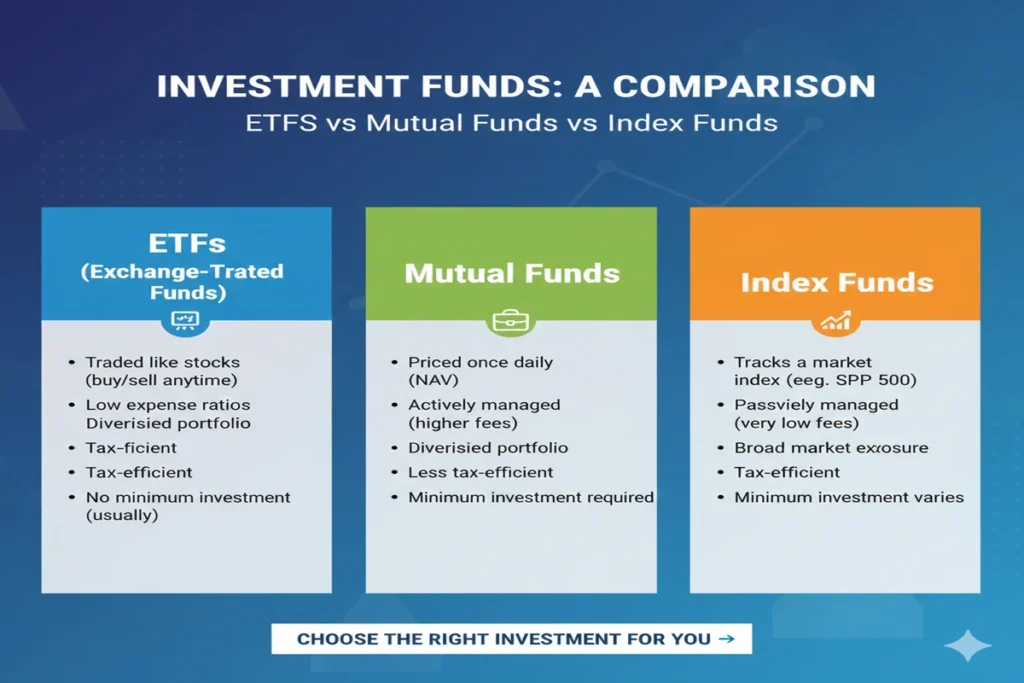
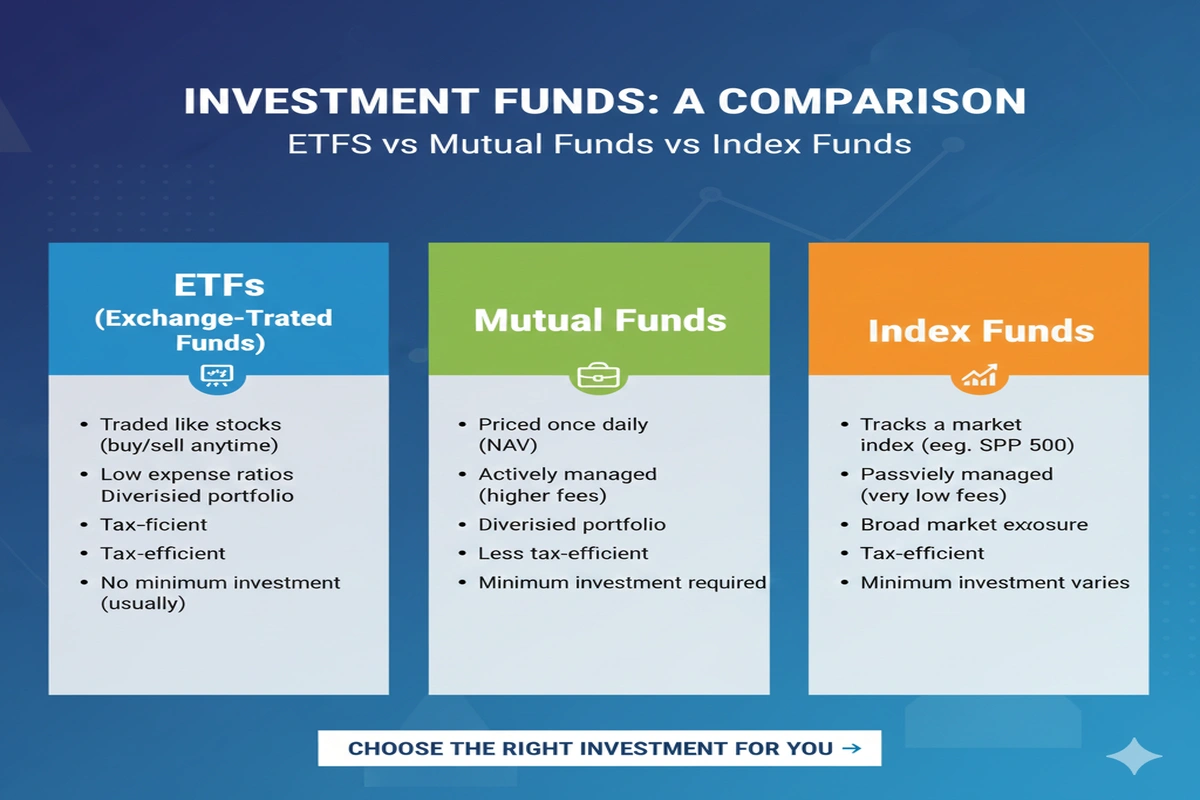
ETF vs Mutual Fund – Key Differences
- Trading Flexibility: ETFs trade all day, mutual funds trade once per day
- Fees: ETFs usually have lower expense ratios
- Tax Efficiency: ETFs are more tax-efficient
- Minimum Investment: ETFs can be bought per share, mutual funds may have higher minimums
- Management: Mutual funds may be actively managed; ETFs are usually passive
Popular Types of ETFs
ETFs Stock
These ETFs invest in a basket of stocks, tracking indices or sectors like technology, healthcare, or S&P 500.
ETFs Gold
Investors gain exposure to gold prices without owning physical gold, acting as a hedge against inflation.
ETFs Vanguard
Vanguard ETFs are low-cost and ideal for long-term diversified investing.
ETFs BlackRock
iShares ETFs from BlackRock offer global exposure across stocks, bonds, and commodities.
How to Choose the Right ETF
- Long-Term Growth: S&P 500 ETFs or ETFs Vanguard
- Inflation Hedge: ETFs gold
- Dividend Income: Stock ETFs focusing on dividend-paying companies
- Diversification: ETFs tracking international markets or multiple sectors
- ETFs to Buy: Check expense ratio, liquidity, historical performance, and fund size
Pros and Cons of ETFs vs Mutual Funds
ETFs Pros
- Trade anytime during market hours
- Low fees and expense ratios
- Tax-efficient
- Diversified and accessible
ETFs Cons
- Requires a brokerage account
- May have trading fees
- Requires some market knowledge
Mutual Fund Pros
- Professional management
- Easier for beginners
- Automatic dividend reinvestment
- Hands-off investing
Mutual Fund Cons
- Higher fees
- Less flexible trading
- Potential capital gains tax liability
Should You Invest in ETFs or Mutual Funds?
If you want flexibility, low costs, and real-time trading, ETFs may be better. If you prefer professional management and don’t mind higher fees, mutual funds are a solid option. Many investors combine both for a balanced portfolio.
ETFs vs Index Funds
Index funds are mutual funds tracking a market index. ETFs can also track indices but trade like stocks, usually with lower fees. Both offer diversification, but ETFs provide more flexibility.
Common Mistakes Investors Make
- Buying ETFs without checking the underlying assets
- Ignoring expense ratios
- Assuming all ETFs are equally diversified
- Failing to align investments with personal goals
Comparison Table: ETFs vs Mutual Funds vs Index Funds
| Feature / Aspect | ETFs | Mutual Funds | Index Funds |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trading Flexibility | Trades all day like stocks | Priced once per day | Priced once per day |
| Management | Usually passive | Often actively managed | Passive, tracks index |
| Fees | Low expense ratios | Higher, especially active funds | Low to moderate |
| Tax Efficiency | High | Lower | High |
| Minimum Investment | Usually per share | Often higher | Often higher |
| Accessibility | Brokerage account required | Direct from fund company | Direct from fund company |
| Diversification | High | High | High |
| Examples | ETFs Vanguard, ETFs BlackRock, ETFs Gold, ETFs Stock | Actively managed equity or bond funds | S&P 500 Index Fund, Nasdaq Index Fund |
| Best For | Flexible investors, low-cost trading | Hands-off investors, professional management | Long-term passive investors |
| Risk Level | Moderate to high | Moderate | Moderate |
FAQs About ETFs and Mutual Funds
- Q: What is the difference between ETFs and mutual funds?
A: ETFs trade like stocks and usually have lower fees. Mutual funds are priced once per day and may be actively managed. - Q: Are ETFs better than mutual funds?
A: ETFs are flexible and tax-efficient. Mutual funds suit investors preferring professional management. - Q: What are ETFs Vanguard and ETFs BlackRock?
A: Popular ETF providers. Vanguard ETFs are low-cost; BlackRock iShares ETFs provide global exposure. - Q: What are the best ETFs to buy in 2025?
A: Depends on goals: stock ETFs for growth, gold ETFs for hedging, Vanguard or BlackRock for diversification. - Q: How are ETFs vs index funds different?
A: Index funds are mutual funds tracking an index; ETFs trade like stocks with lower fees.
Conclusion
ETFs and mutual funds are both excellent investment options. ETFs offer flexibility, low fees, and real-time trading. Mutual funds provide professional management and convenience. Understanding ETF vs mutual fund and using ETFs like Vanguard, BlackRock, gold, or stock ETFs will help you make smart investment choices in 2025.
Leave a Reply